





+
+
.7★
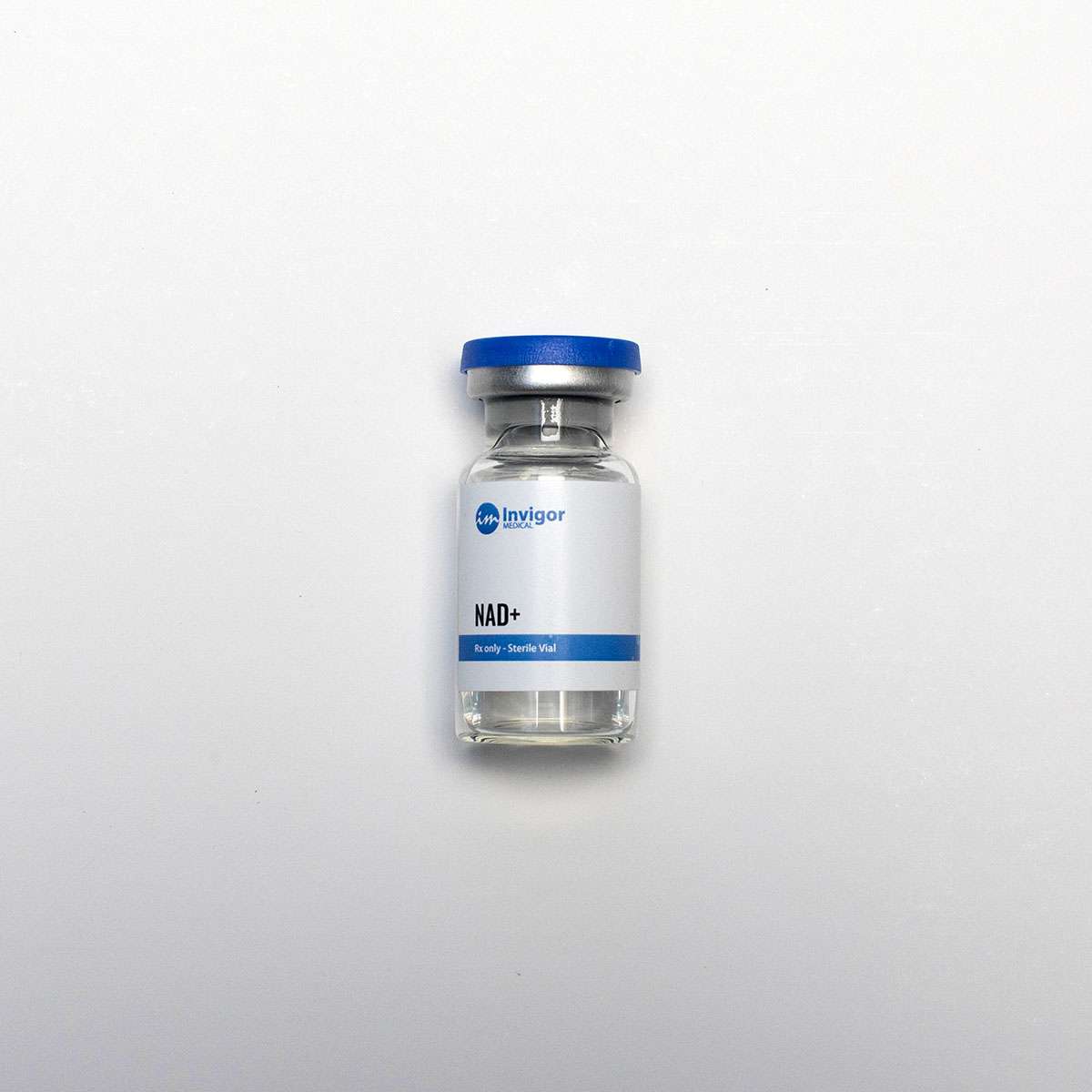


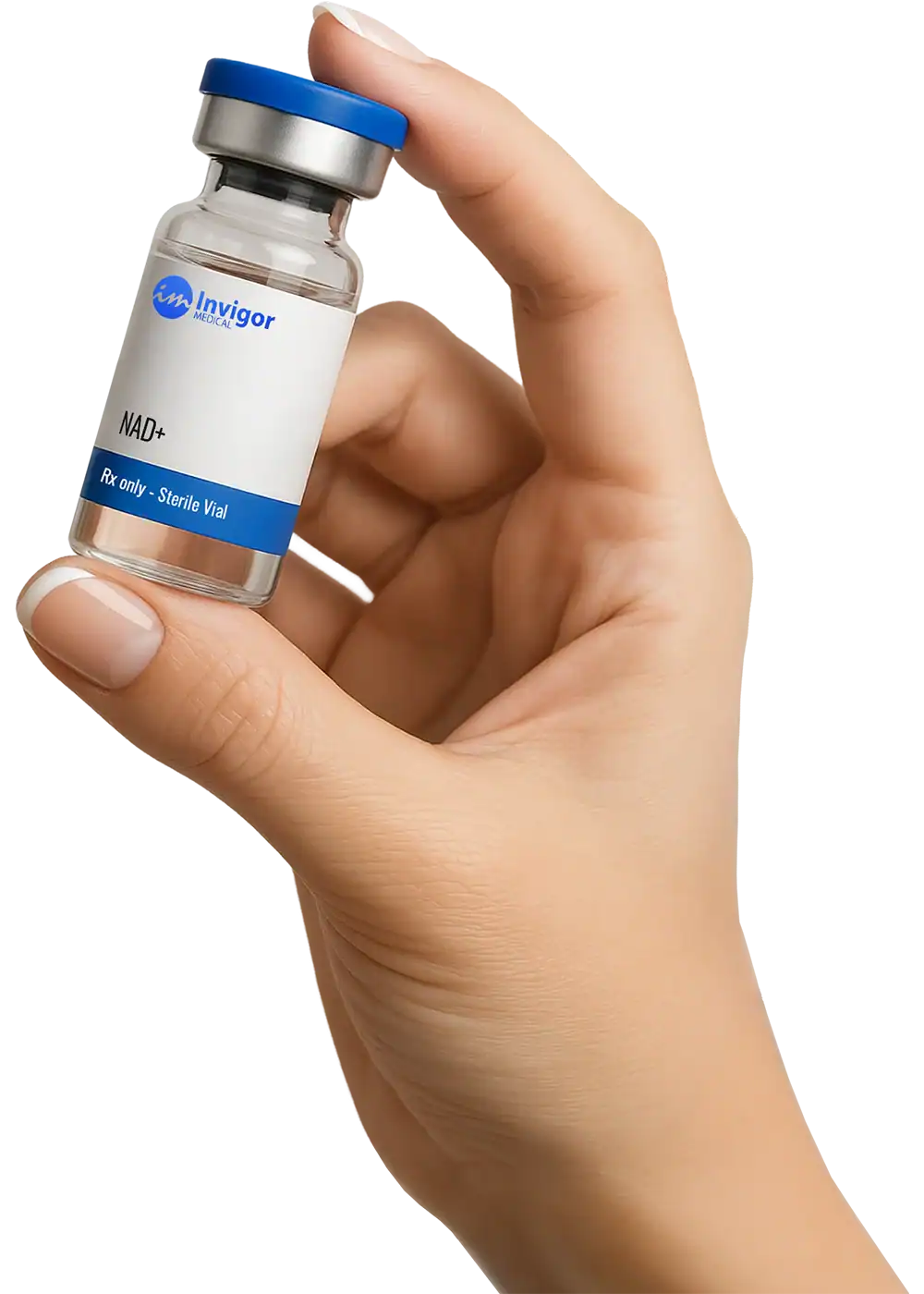
Yes. Although NAD+ was only available to be administered via an IV, NAD+ is now compounded by pharmacies for delivery via subcutaneous injection.
NAD+ is often prescribed at a starting dosage of 200-300mcg daily. However, you should consult with a physician before you determine if NAD+ is right for you.
Several clinical trials (36 completed) have assessed the effectiveness and safety of NAD+ use for treating symptoms associated with aging and aging-related disease. No study reported severe side effects. Therefore, NAD+ is considered “likely to be safe.”
More side effects may be expected at higher doses, such as liver injury in susceptible people, headaches, skin flushing, and dizziness.
There are several lifestyle changes you can make to increase NAD+, including:
NAD+ is considered “likely to be safe.” With that said, any medication has the potential to cause side effects in susceptible people. Potential side effects of NAD+ include:
Foods that are high in antioxidants and niacin increase NAD+ levels. Consume more of the following foods:
Vitamin B3 is a precursor for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD). There are several ways that your body makes NAD. One way is from the essential amino acid tryptophan. This process requires vitamin B3.
High levels of NAD+ are needed for exercise, and exercise stimulates the production of NAD+.
NAD+ is essential for producing cellular energy. During periods of strenuous or prolonged exercise, there is increased demand for energy. NAD+ is needed to produce glucose in the liver and break down fats for energy.
NAD+ is also a signaling molecule that tells DNA to increase transcription and translation to produce more proteins than the cells need to produce energy.
NAD+ is also needed in the muscle to reduce the oxidative stress incurred from increased metabolism.
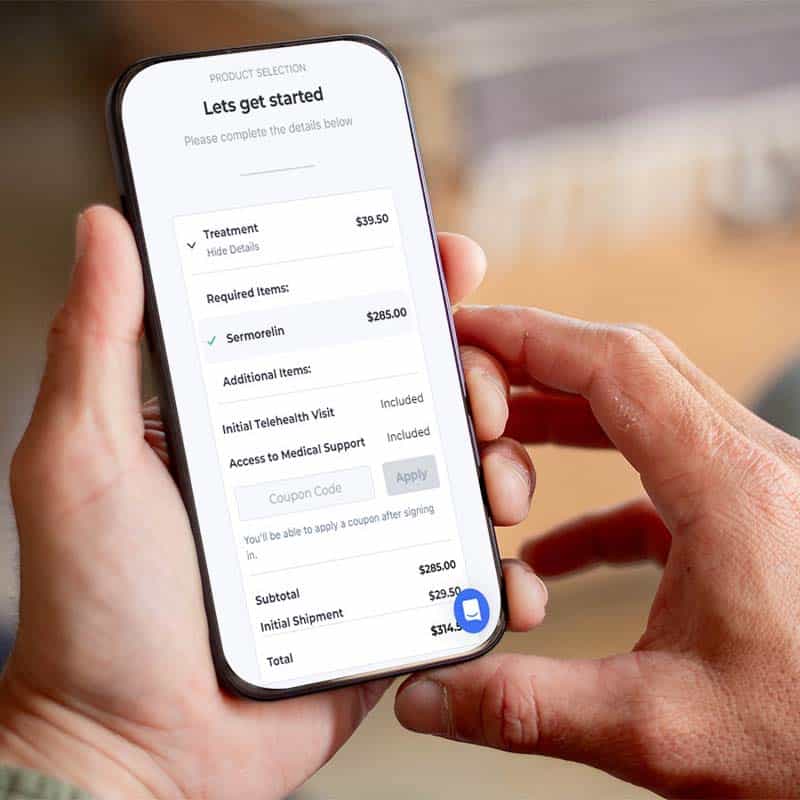





*Prescription medications available only if prescribed by the healthcare provider after an online consultation. This is a compounded medication.